TDM Over IP Connectivity
TDM over IP
Key Features
![]() Carry telephone tie-lines across private data networks
Carry telephone tie-lines across private data networks
![]() Backhaul of voice channels from cellular base stations to MTSO
Backhaul of voice channels from cellular base stations to MTSO
![]() Rural telephony transmission systems
Rural telephony transmission systems
![]() Private E1/T1 line (TDM) over IP network
Private E1/T1 line (TDM) over IP network
![]() Bypass international telephone tolls
Bypass international telephone tolls
![]() Couple with Ethernet radios for a wireless E1/T1 link
Couple with Ethernet radios for a wireless E1/T1 link
The TDM over IP Gateway transparently carries E1 or T1 formatted TDM circuits across a packet switch network and reconstitutes it on the other side with minimum latency. This is NOT "Voice-over-IP". With TDM over IP you get a fully transparent circuit which maintains all signaling of the TDM frame, therefore supporting high-speed modems, FAX and voice channels with no loss of quality.
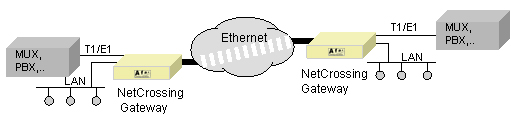
We are using Afar NetCrossing Gateway breaks the E1 or T1 serial data streams into fixed size packets, adds the Ethernet or IP framing, and sends them over a packet switch network to a remote gateway. At the remote end, the gateway removes the Ethernet or IP framing and reconstructs the original T1 or E1 data stream.
The receiving NetCrossing gateway buffers a number of incoming packets in order to compensate for the packet delivery jitter introduced by the network. The size of this buffer is configurable to accommodate different amounts of expected jitter. The unit collects statistics of the network jitter, and can automatically optimize the buffer size for minimal link latency. If the capacity of the packet switch network is abundant, you can transport two full E1 circuits. If the capacity is limited you can specify a subset of channels from a combination of the two E1/T1 lines. The link capacity that is not used by the TDM circuit(s) can be used for Ethernet bridging through a LAN port on the unit. The gateway gives priority to the TDM data, and measures out a limited amount of LAN data traffic that will fit beside the TDM channels within the declared network capacity. This is useful, for example, if the network is a radio link with limited throughput.
The NetCrossing gateway can also be paired with Ethernet high speed radios to deploy E1 / T1 wireless links for a fraction of the cost of an equivalent microwave transmission system.